README
SuccessForge: An AI-Powered Multi-Agent Framework for D365 Finance & Supply Chain Management Implementations
Forging Implementation Excellence Through Large Language Models and Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Executive Summary
Implementing Microsoft Dynamics 365 Finance and Supply Chain Management (D365 FSCM) is a complex undertaking that typically requires months of planning, coordination between multiple specialists, and continuous knowledge management. SuccessForge addresses these challenges by introducing an AI-powered multi-agent orchestration framework that combines specialized AI agents with a domain-specific knowledge base.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of SuccessForge’s background, architecture, agent roles, and the outputs it generates to support D365 FSCM implementation projects.
1. Background and Motivation
The Challenge of D365 FSCM Implementations
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) implementations remain among the most challenging IT projects. According to industry research, ERP projects frequently exceed budgets and timelines, with success rates varying significantly based on methodology adherence and team expertise.
Microsoft’s Success by Design framework provides a structured approach to D365 implementations, defining four key phases: Initiate, Implement, Prepare, and Operate. Each phase requires specific deliverables, stakeholder coordination, and domain expertise spanning project management, solution architecture, and technical research.
The Knowledge Problem
Implementation teams face a recurring challenge: critical knowledge is scattered across multiple sources including Microsoft documentation, internal project artifacts, best practice guides, and lessons learned from previous engagements. Team members spend significant time searching for information rather than applying their expertise to solve problems.
A Real-World Example: The RfP Process
Consider the Request for Proposal (RfP) phase — often the first critical milestone in a D365 implementation engagement. A typical RfP response requires coordinated input from multiple specialists within tight deadlines:
The Scenario
A manufacturing company issues an RfP for a D365 Finance & Supply Chain Management implementation. The consulting firm has 3 weeks to respond. The RfP contains 150+ questions spanning functional requirements, technical architecture, project methodology, pricing, and references.
The Traditional Approach
| Role | Tasks | Time Spent |
|---|---|---|
| Bid Manager | Coordinate responses, manage timeline, ensure compliance | 40+ hours |
| Solution Architect | Design technical architecture, integration strategy, environment plan | 30+ hours |
| Functional Consultants | Answer module-specific questions (Finance, SCM, Manufacturing) | 50+ hours |
| Project Manager | Develop project plan, resource estimates, risk assessment | 25+ hours |
| Research/Presales | Gather case studies, competitive analysis, Microsoft roadmap | 20+ hours |
The Pain Points
- Knowledge Fragmentation: Answers to similar questions exist in previous proposals, but finding them requires searching through dozens of documents
- Consistency Risk: Different team members provide varying answers to related questions
- Time Pressure: Subject matter experts are pulled from billable projects to support RfP responses
- Institutional Knowledge Loss: When experienced consultants leave, their RfP expertise leaves with them
- Repetitive Research: Teams repeatedly research the same Microsoft documentation for standard questions
How SuccessForge Transforms This Process
With SuccessForge, the RfP response becomes a structured, AI-assisted workflow:
# RfP Response: Contoso Manufacturing D365 Implementation
## Context
Customer: Contoso GmbH (Manufacturing, 850 employees)
Current ERP: SAP ECC 6.0 (end of support 2027)
Budget: 1.5M EUR | Timeline: 18 months
Key Requirements: Finance, SCM, Salesforce integration
## RfP Questions
### Section 3: Technical Architecture
Q3.1 @architect Describe your proposed integration architecture
for connecting D365 with the customer's existing Salesforce CRM.
Q3.2 @architect What is your recommended environment strategy
(DEV, TEST, UAT, PROD) and how does it align with Microsoft LCS?
Q3.3 @research What are the current Microsoft-recommended patterns
for D365-Salesforce integration? Include Dual-Write and Dataverse options.
### Section 4: Project Methodology
Q4.1 @pm Provide a high-level project plan with phases, milestones,
and key deliverables following Success by Design methodology.
Q4.2 @pm What are the top 5 risks for this type of implementation
and your proposed mitigation strategies?
Q4.3 @pm How do you ensure knowledge transfer to the customer's
internal IT team during and after the implementation?
### Section 5: Functional Capabilities
Q5.1 @research Which D365 Finance modules are most relevant for
a discrete manufacturing company? List key features.
Q5.2 @architect How would you approach data migration from a
20-year-old SAP system with potential data quality issues?
The Result
Processing this question catalog through SuccessForge:
- Research Agent retrieves current Microsoft documentation, ISV options, and best practices from the knowledge base
- Solution Architect Agent generates architecture recommendations aligned with Microsoft patterns and the customer’s specific landscape
- Project Manager Agent produces methodology-compliant project plans with Success by Design phase alignment
- All answers are automatically documented in the source file, creating a reusable RfP response template
Measurable Impact
| Metric | Traditional | With SuccessForge |
|---|---|---|
| Initial draft time | 2–3 weeks | 2–3 days |
| SME hours required | 150+ hours | 40–50 hours |
| Consistency across answers | Variable | High (shared context) |
| Knowledge reuse | Manual search | Automatic RAG retrieval |
| Response template creation | Manual | Automatic |
The RfP example illustrates SuccessForge’s core value proposition: transforming fragmented expertise into systematic, repeatable knowledge capture.
SuccessForge’s Approach
SuccessForge was developed to address these challenges through two complementary capabilities:
Specialized AI Agents: Role-specific agents that embody the expertise of project managers, solution architects, and researchers, each with tailored system prompts aligned to Microsoft’s Success by Design methodology.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): A semantic search layer that enables agents to query project-specific documents and a global knowledge base containing D365 implementation guides, business process catalogs, and best practices.
2. System Architecture
2.1 Architectural Overview
SuccessForge follows a modular, layered architecture designed for flexibility and extensibility:
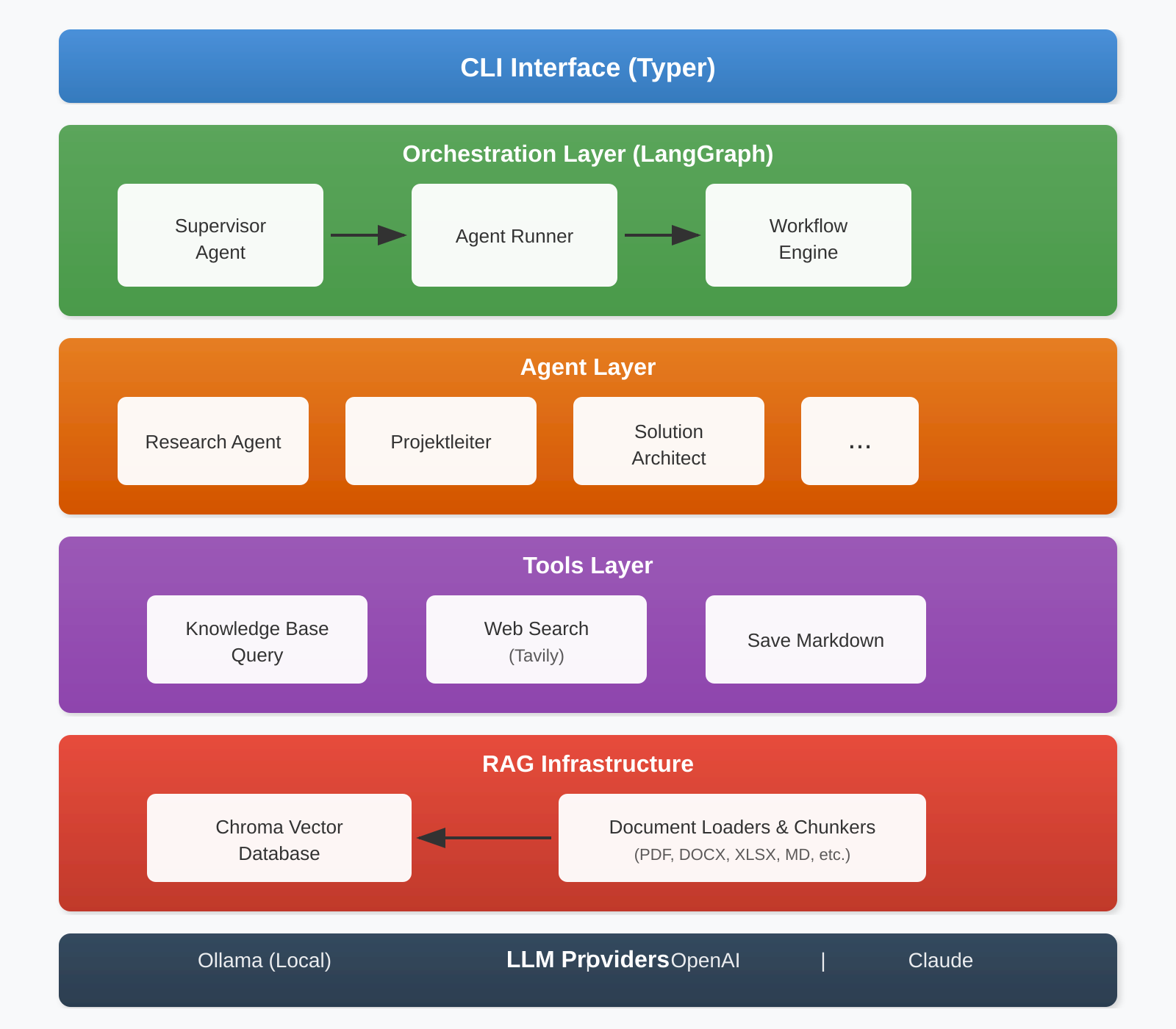
2.2 Core Technology Stack
| Component | Technology | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| CLI Framework | Typer + Rich | Command-line interface with formatted output |
| Agent Orchestration | LangGraph | State-machine based workflow management |
| LLM Integration | LangChain | Unified interface to multiple LLM providers |
| Vector Database | Chroma | Semantic search and document retrieval |
| Embeddings | Ollama (embeddinggemma) | Local embedding generation |
| Web Search | Tavily | Real-time information retrieval |
2.3 Configuration Architecture
Agent configurations are externalized into YAML files, enabling non-technical users to adjust LLM providers, models, and tool assignments without code changes:
agents:
research:
name: "Research Agent"
llm_provider: "ollama"
model: "gpt-oss:120b-cloud"
temperature: 0.3
tools:
- "web_search"
- "query_knowledge_base"
- "save_markdown"
projektleiter:
name: "Projektleiter"
llm_provider: "openai"
model: "gpt-4.1"
tools:
- "all"
System prompts are stored as Markdown files in a dedicated roles/ directory, allowing domain experts to refine agent behavior without developer involvement.
3. Agent Roles and Responsibilities
SuccessForge implements a hierarchical multi-agent system where each agent embodies a specific role within a D365 implementation team. This design mirrors real-world project structures and ensures domain-appropriate responses.
3.1 Supervisor Agent
Purpose: Orchestration and task delegation
The Supervisor Agent analyzes incoming requests and routes them to the appropriate specialist agent. For complex tasks requiring multiple perspectives, it can invoke multiple agents sequentially and synthesize their outputs into a coherent response.
Key Capabilities:
- Task analysis and decomposition
- Agent selection based on query context
- Result aggregation and synthesis
- Cross-agent coordination
3.2 Research Agent
Purpose: Information retrieval and knowledge synthesis
The Research Agent serves as the team’s knowledge specialist, responsible for gathering information from both internal knowledge bases and external sources.
Key Capabilities:
- Semantic search across project documents
- Web search for current information (Microsoft documentation, release notes, community insights)
- Best practice compilation
- Technology assessment and comparison
Aligned Success by Design Activities:
- Industry analysis (RS-I-001)
- Best practice collection (RS-I-002)
- Microsoft roadmap analysis (RS-I-003)
- ISV landscape research (RS-I-004)
3.3 Projektleiter (Project Manager) Agent
Purpose: Project planning and governance
The Projektleiter Agent embodies the expertise of an experienced D365 project manager, with deep knowledge of Microsoft’s Success by Design methodology.
Key Capabilities:
- Project charter development
- Governance framework design
- Risk assessment and mitigation planning
- Stakeholder communication planning
- Change management coordination
Aligned Success by Design Activities:
- Project charter creation (PM-I-001)
- Governance establishment (PM-I-002)
- Project plan development (PM-I-003)
- Risk assessment (PM-I-004)
- Sprint planning and monitoring (PM-IM-001, PM-IM-002)
- Go-Live readiness assessment (PM-P-001)
3.4 Solution Architect Agent
Purpose: Technical design and quality assurance
The Solution Architect Agent provides technical leadership, ensuring solutions align with Microsoft best practices while meeting business requirements.
Key Capabilities:
- Solution blueprint development
- Fit-Gap analysis
- Integration architecture design
- Technical risk identification
- Performance and scalability planning
Aligned Success by Design Activities:
- Solution Blueprint creation (SA-I-001)
- Fit-Gap analysis (SA-I-002)
- Integration landscape analysis (SA-I-003)
- Technical risk assessment (SA-I-004)
- Environment strategy definition (SA-I-005)
4. The Heart of SuccessForge: Role Descriptions as Encoded Expertise
While the technology stack enables SuccessForge’s capabilities, the role descriptions are what transform generic AI into domain-specific expertise. These comprehensive Markdown documents serve as the “DNA” of each agent, encoding years of implementation experience into structured, actionable knowledge.
4.1 Anatomy of a Role Description
Each role description follows a rigorous structure aligned with Microsoft’s Success by Design methodology. Taking the Projektleiter (Project Manager) role as an example, a single role file spans over 1,700 lines and includes:
Process Definitions with Full Traceability
PROZESS: Projektcharter erstellen
VERSION: 1.0
PHASE: Initiate
PROZESS-ID: PM-I-001
TRIGGER:
- Vertragsunterzeichnung abgeschlossen
- Projektauftrag erteilt
INPUT:
- Vertragsdokumente
- Statement of Work (SOW)
- Kundenanforderungen (High-Level)
SCHRITTE:
1. Vertragsinhalte analysieren
- Scope-Grenzen identifizieren
- Liefergegenstände auflisten
...
OUTPUT:
- Genehmigter Projektcharter
- Stakeholder-Register
- Initiale Erfolgskriterien
QUALITÄTSKRITERIEN:
- Alle Pflichtfelder ausgefüllt
- Unterschriften aller Schlüssel-Stakeholder
ESKALATION:
- Bei fehlender Genehmigung > 5 Arbeitstage: Eskalation an Sponsor
4.2 Impact on Agent Behavior
The depth of these role descriptions directly influences output quality:
| Aspect | Impact |
|---|---|
| Process IDs | Agents reference specific processes (e.g., “Following PM-I-003”), enabling traceability |
| Trigger Conditions | Agents understand when to recommend specific activities |
| Input/Output Definitions | Responses include concrete deliverable expectations |
| Quality Criteria | Agents can validate completeness of proposed solutions |
| Escalation Paths | Risk-aware recommendations with clear escalation thresholds |
| KPIs & Metrics | Quantitative targets embedded in recommendations (e.g., “SPI >= 0.95”) |
| Interface Definitions | Agents understand handoffs between roles (PM ↔ Solution Architect) |
4.3 Why This Matters
Traditional AI assistants provide generic responses based on broad training data. SuccessForge agents, in contrast, operate within a constrained expertise framework:
- A Projektleiter agent doesn’t just “know about project management” — it knows that Risk Assessment (PM-I-004) must follow Project Plan Development (PM-I-003)
- A Solution Architect agent understands that Fit-Gap Analysis (SA-I-002) requires specific outputs: Fit-Gap Matrix, Gap-Lösungsempfehlungen, Aufwandsschätzung
- Responses align with Success by Design phases (Initiate → Implement → Prepare → Operate)
The role descriptions transform AI from a general assistant into a methodology-compliant specialist.
5. Knowledge Base and RAG Infrastructure
5.1 Dual Knowledge Base Architecture
SuccessForge maintains two distinct knowledge bases:
Project-Specific Knowledge Base
- Contains documents related to active implementation projects
- Supports project ID filtering for multi-project environments
- Stores requirements documents, meeting notes, design specifications
Global Knowledge Base
- Houses D365 documentation and implementation guides
- Includes Success by Design delivery plans and process catalogs
- Contains industry best practices and lessons learned
5.2 Supported Document Formats
The RAG pipeline processes a comprehensive range of document formats common in enterprise environments:
| Category | Formats |
|---|---|
| Text | .md, .txt |
| Documents | .pdf, .docx, .doc |
| Spreadsheets | .xlsx, .xls |
| Presentations | .pptx, .ppt |
| Data | .json, .xml, .csv |
| Web | .html |
5.3 Intelligent Chunking
Documents are processed using semantic chunking that preserves contextual boundaries:
- Semantic Chunker: For narrative content (guides, specifications), uses embedding-based breakpoint detection to maintain coherent chunks
- Recursive Character Splitter: For structured content (tables, data files), uses hierarchical separators with overlap for context preservation
6. System Outputs
SuccessForge generates several categories of outputs to support implementation teams:
6.1 Interactive Query Responses
Users can query specific agents using mention syntax:
# Query the Research Agent
ask "@research What are the key considerations for D365 Finance data migration?"
# Query the Solution Architect
ask "@Architect Design an integration pattern for connecting D365 with our CRM system"
# Query the Project Manager
ask "@pm Create a risk assessment framework for our go-live phase"
6.2 The Question Catalog: Structured Knowledge Elicitation
The Question Catalog (implemented via the Markdown Processor) represents a paradigm shift from ad-hoc queries to systematic knowledge capture. Rather than asking isolated questions, teams define structured questionnaires that leverage the full power of SuccessForge’s multi-agent architecture.
How It Works
Input: A Markdown file combining context, questions, and agent assignments:
# Project Analysis: Manufacturing ERP Implementation
## Context
We are implementing D365 Finance for a mid-sized manufacturing
company with 500 employees. Current systems include a legacy
ERP (20+ years old), standalone MES, and Excel-based planning.
## Questions
1. @research What are manufacturing-specific D365 features
relevant to discrete manufacturing?
2. @Architect Based on the legacy landscape described above,
what integration pattern should we use for shop floor systems?
3. @pm Considering this is a legacy replacement project,
what are the key risks during the Implement phase?
4. @Architect How should we approach data migration from a
20-year-old system with potential data quality issues?
Output: The same document, enriched with comprehensive AI-generated answers inserted directly below each question.
Why Question Catalogs Matter
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Context Inheritance | All questions receive the same project context, ensuring consistency |
| Agent Specialization | Each question routes to the most qualified specialist via @mentions |
| Documentation by Design | Answers are automatically documented — no copy-paste required |
| Iterative Refinement | Teams can re-run catalogs as project understanding deepens |
| Knowledge Baseline | Creates a searchable record of project decisions and rationale |
| Onboarding Accelerator | New team members can review Q&A documents to understand project history |
Practical Applications
Project Kickoff Catalog: Standard questions for every new engagement
1. @research What industry-specific regulations apply?
2. @Architect What are typical integration points for this industry?
3. @pm What Success by Design milestones apply to this project size?
Design Review Catalog: Technical validation questions
1. @Architect Does this design follow Microsoft best practices?
2. @research Are there ISV solutions that address this gap?
3. @pm What is the change management impact of this design decision?
Go-Live Readiness Catalog: Pre-launch verification
1. @pm Are all Go-Live Readiness criteria from PM-P-001 addressed?
2. @Architect What technical risks remain unmitigated?
3. @research What lessons learned from similar go-lives should we consider?
The Question Catalog transforms SuccessForge from a reactive Q&A tool into a proactive knowledge generation system that aligns with project milestones and governance requirements.
6.3 Chat Mode with Context Preservation
For iterative exploration, the chat mode maintains conversation history:
chat --project 99
This enables follow-up questions that build on previous responses, supporting deep-dive analysis sessions.
6.4 Orchestrated Multi-Agent Responses
For complex queries requiring multiple perspectives, the orchestration mode engages the Supervisor to coordinate specialist agents:
orchestrate "Develop a comprehensive data migration strategy for our ERP replacement project"
The Supervisor delegates subtasks to appropriate agents and synthesizes a unified response.
7. Getting Started: The Setup Process
Deploying SuccessForge requires configuring five interconnected components. This section provides an overview of each component’s role in the system.
7.1 Environment Configuration (.env)
The environment file contains API keys for LLM providers and research tools:
# LLM Provider Keys
ANTHROPIC_API_KEY=sk-ant-... # For Claude models
OPENAI_API_KEY=sk-proj-... # For GPT-4 models
# Local LLM (Ollama)
OLLAMA_MODEL=gpt-oss:120b-cloud
OLLAMA_BASE_URL=http://localhost:11434
# Research Tools
TAVILY_API_KEY=tvly-... # Web search capability
Impact: Without valid API keys, agents cannot invoke their underlying LLMs. The system supports fallback between providers if one is unavailable.
7.2 Agent Configuration (config/agents.yaml)
This YAML file defines the “personality” of each agent:
agents:
projektleiter:
name: "Projektleiter"
role_file: "projektleiter.md" # Links to role description
llm_provider: "openai"
model: "gpt-4.1"
temperature: 0.3 # Lower = more consistent
tools:
- "all"
Impact: Changing llm_provider or model allows teams to balance cost, speed, and capability. The role_file reference connects agents to their detailed role descriptions.
7.3 Knowledge RAG (Global Knowledge Base)
The Knowledge RAG contains D365 documentation that applies across all projects:
# Import Microsoft documentation and best practices
python main.py RAG knowledge-import ./knowledge/
Typical Contents:
- D365 Implementation Guide (PDF)
- Success by Design Delivery Plans (XLSX)
- Business Process Catalogs (XLSX)
- Microsoft Best Practice Documentation
Impact: This knowledge base enables agents to provide answers grounded in official Microsoft guidance, regardless of which project they’re working on.
7.4 Project RAG (Project-Specific Documents)
Each project has its own document collection, isolated by Project ID:
# Import project documents with Project ID 99
python main.py RAG import ./Projects/Contoso_D365/ --project 99
Typical Contents:
- Requirements documents
- Meeting notes and decisions
- Design specifications
- Data mapping spreadsheets
Impact: When querying with --project 99, agents search both the global knowledge base AND the project-specific documents, providing contextually relevant answers.
7.5 Question Catalogs (Fragenkatalog)
Pre-defined questionnaires enable systematic knowledge capture:
# Project Kickoff Questions
## Context
Manufacturing company, 850 employees, SAP to D365 migration.
## Questions
1. @research What D365 modules are relevant for manufacturing?
2. @Architect Design the integration architecture for Salesforce.
3. @pm Create a risk register following Success by Design.
# Process the catalog
python main.py Agents process-file ./kickoff_questions.md --project 99
Impact: Question catalogs transform SuccessForge from an interactive Q&A tool into a documentation generation system. Answers are inserted directly into the source file, creating a persistent record of decisions and rationale.
Setup Flow Diagram
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 1. ENVIRONMENT (.env) │
│ API Keys: Anthropic, OpenAI, Tavily │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 2. AGENT CONFIG (agents.yaml) │
│ Maps agents → LLMs → Role Files → Tools │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
│
┌───────────────┴───────────────┐
▼ ▼
┌──────────────────────────┐ ┌──────────────────────────┐
│ 3. KNOWLEDGE RAG │ │ 4. PROJECT RAG │
│ Global D365 Docs │ │ Project Documents │
│ (applies to all) │ │ (filtered by ID) │
└──────────────────────────┘ └──────────────────────────┘
│ │
└───────────────┬───────────────┘
▼
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 5. QUESTION CATALOGS │
│ Structured queries → Documented answers │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
8. Practical Applications
8.1 Project Initiation Support
During the Initiate phase, teams can use SuccessForge to:
- Generate initial project charters based on scope descriptions
- Research industry-specific D365 implementations
- Develop governance framework recommendations
- Create risk registers aligned with Success by Design
8.2 Design Phase Acceleration
During the Implement phase:
- Conduct fit-gap analysis against documented requirements
- Research integration patterns for specific scenarios
- Generate technical specifications based on architectural decisions
- Produce best practice recommendations for specific configurations
8.3 Knowledge Preservation
Throughout the project lifecycle:
- Capture decisions and rationale in searchable format
- Build project-specific knowledge bases for future reference
- Enable rapid onboarding of new team members
- Preserve lessons learned for organizational benefit
9. Future Directions
SuccessForge establishes a foundation for continued enhancement:
- Additional Agent Specializations: Functional consultants, data migration specialists, change management experts
- Automated Documentation Generation: Direct production of project deliverables from agent interactions
- Integration with Project Management Tools: Bidirectional sync with Azure DevOps, Microsoft Project
- Multi-Language Support: Extend beyond German/English to support global implementation teams
Conclusion
SuccessForge represents a practical application of AI technology to the complex domain of enterprise ERP implementation. By combining specialized AI agents with retrieval-augmented generation, the framework addresses the persistent challenges of knowledge management, expertise accessibility, and methodology adherence that impact D365 FSCM projects.
The multi-agent architecture mirrors real-world team structures, ensuring that AI assistance aligns with established implementation methodologies. The externalized configuration approach enables continuous refinement of agent behaviors without code changes, supporting iterative improvement based on practical experience.
For organizations undertaking D365 FSCM implementations, SuccessForge offers a framework for augmenting human expertise with AI capabilities, potentially accelerating project timelines while maintaining alignment with Microsoft’s Success by Design principles.
For technical documentation and implementation details, refer to the project repository.